Generative Engine Optimization: The Complete Guide to Dominating AI Search in 2025
1. Defining and Contextualising GEO
Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) is the practice of optimising content so that it is prominently featured in AI-generated search results, in other words, making sure your website’s information is picked up and used by AI-driven search engines and chatbots.
Unlike traditional SEO (which focuses on improving your rank in a list of blue links on a search engine results page), GEO is about ensuring your content is recognised and synthesised by large language models (LLMs) when they answer user queries. In practical terms, GEO means structuring and writing your digital content such that AI systems like ChatGPT, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), Bing Chat, Gemini, Claude, or Perplexity can easily understand it and include it (often with citations) in their conversational answers to users.
This shift is becoming crucial because user search behaviour is rapidly evolving toward AI-powered “answer engines.” Consumers increasingly ask questions to AI chatbots or generative search interfaces and get direct answers, rather than clicking through multiple websites.
Recent research from Bain & Company finds that about 80% of search users now rely on AI-written results for at least 40% of their searches, contributing to an estimated 15–25% reduction in organic web traffic. Google's own generative AI feature ("AI Overviews") serves complete answers to over 1.5 billion users monthly, with Bain finding that 60% of searches now terminate without users clicking through to another website.
However, the current impact varies significantly across different metrics and timeframes. While Bain's consumer behaviour research shows substantial reliance on AI summaries, other data indicates that AI-specific search traffic still represents less than 1% of total website traffic for most sites as of mid-2025. This suggests that while user behaviour and expectations are changing rapidly, the complete transition to AI-dominated search is still in progress, with traditional search maintaining significant importance in the near term.
In this evolving context, even if your site ranks well on traditional Google, it may become less visible to users who increasingly turn to AI assistants and chat-style search instead of classic search engines. GEO has emerged to address this reality: it's about staying visible and relevant across both traditional and AI-driven search experiences – meeting your audience where they search now while preparing for the continued evolution toward AI-driven interfaces that deliver instant, conversational answers.
2. The Current Landscape of Generative AI Search
The rise of generative AI search engines and assistants has transformed how information is retrieved, processed, and presented. Traditional search engines (like classic Google or Bing) return a ranked list of links for the user to browse. By contrast, generative AI search engines produce a single, synthesised answer – often in paragraph form or a conversational style – pulling information from many sources and presenting it as a cohesive response.
For example, Bing Chat (powered by GPT-4) will web search for you and then compile the findings into a written answer with footnoted citations. Google's SGE integrates a similar AI-generated summary at the top of its results, with key points and links embedded. ChatGPT (OpenAI) now includes comprehensive web search capabilities available to all users as of February 2025, delivering conversational answers with real-time information and source links. Google's Gemini (formerly Bard) likewise attempts to directly answer queries in dialogue form. Claude (Anthropic) recently gained web search capabilities in March 2025, currently available to paid users, allowing it to access current information and provide sourced responses. Perplexity AI, a newer engine, always responds with a short answer and includes source citations for each sentence. In all these cases, the user experience is Q&A-driven and highly contextual; the AI uses natural language understanding to interpret the query and provide a direct explanation or advice, often referencing multiple web sources rather than sending the user to one particular page.
Because of this approach, generative engines “read” and interpret your content differently than a traditional search crawler would. They don’t just match keywords to pages; instead, they attempt to understand the context and meaning of content using their trained language models. They might break a user query into sub-questions, retrieve relevant passages from various pages, and then compose a unified answer in real time. Notably, many of these AI systems will cite sources (especially for factual claims) to maintain credibility and reduce hallucination, but the citation is often just a footnote or hyperlink rather than a prominent listing. This means that your content could be used to answer a question without the user ever visiting your site – the AI may quote or paraphrase it within the answer. For instance, if someone asks an AI assistant, “What’s the best CRM software for a small business?”, the assistant might say, “According to various sources, the top recommendation is XYZ CRM for its ease of use…” and possibly footnote your blog if it drew info from it. The user gets the answer immediately. As a result, we see dramatically lower click-through rates on many informational searches – Bain & Company research confirms that about 60% of searches now end without any click to a website, because the answer was provided directly on the results page.
The major generative AI platforms each have their nuances. ChatGPT now provides comprehensive web search capabilities to all users as of February 2025, actively showing sources and citations when using search functionality, moving beyond its previous reliance primarily on trained knowledge. Bing Chat and Perplexity are more source-focused; they visibly cite and link to pages, which is an opportunity for traffic if your site is referenced. Google’s SGE blends AI answers with the traditional search interface, highlighting key points and linking out to sources (often favouring sites with good structured data or well-recognised authority). Google's Gemini provides citations for many answers, especially where it directly uses web content. Claude now offers web search capabilities as of March 2025 for paid users, allowing it to access current information with proper source attribution, moving beyond its previous limitation as primarily a Q&A assistant. Across the board, these AI systems emphasise natural language: users are querying in full questions or conversational phrases (“what is the safest family car under $30k?”) more than they would in a classic search box. The AIs also have the capability (present or on the horizon) to incorporate personal context, for example, recalling your previous questions or known preferences, to tailor the answer. This means search results are becoming dynamic and personalised narratives rather than static lists of links.
From a market standpoint, the adoption of generative search is skyrocketing. ChatGPT has reached approximately 800 million weekly active users as of July 2025, with over 122 million daily users globally, establishing it as one of the most rapidly adopted consumer applications in history. Alternative engines are proliferating as well. Perplexity AI has experienced significant growth, reaching approximately 15 million monthly active users, accompanied by substantial increases in user engagement. In 2023 alone, it served over 500 million queries and handled 250 million queries in July 2024.
Meanwhile, Google is rapidly rolling out SGE, and Microsoft has deeply integrated AI into Bing and even Windows (Copilot). While comprehensive consumer trust data varies, early indicators suggest growing acceptance of AI-generated search results, particularly among younger demographics who are more likely to adopt new technologies. Business leaders have noticed these shifts: Gartner predicts traditional search volume will drop 25% by 2026, with some analysts suggesting even greater long-term impacts as users increasingly switch to AI-based search interfaces. In response, companies are starting to retool their digital strategies from classic SEO toward GEO. As Forbes reports, many teams are now "shifting from SEO to GEO," recognising that the rules of visibility have changed – instead of fighting for Position #1 on Google, the goal is to be the snippet or source that an AI chooses to include in its one answer
3. GEO Strategies and Best Practices
Generative Engine Optimization requires a blend of traditional SEO wisdom and new tactics tailored to AI. Below are key strategies (both content-focused and technical) that have emerged as best practices for GEO.
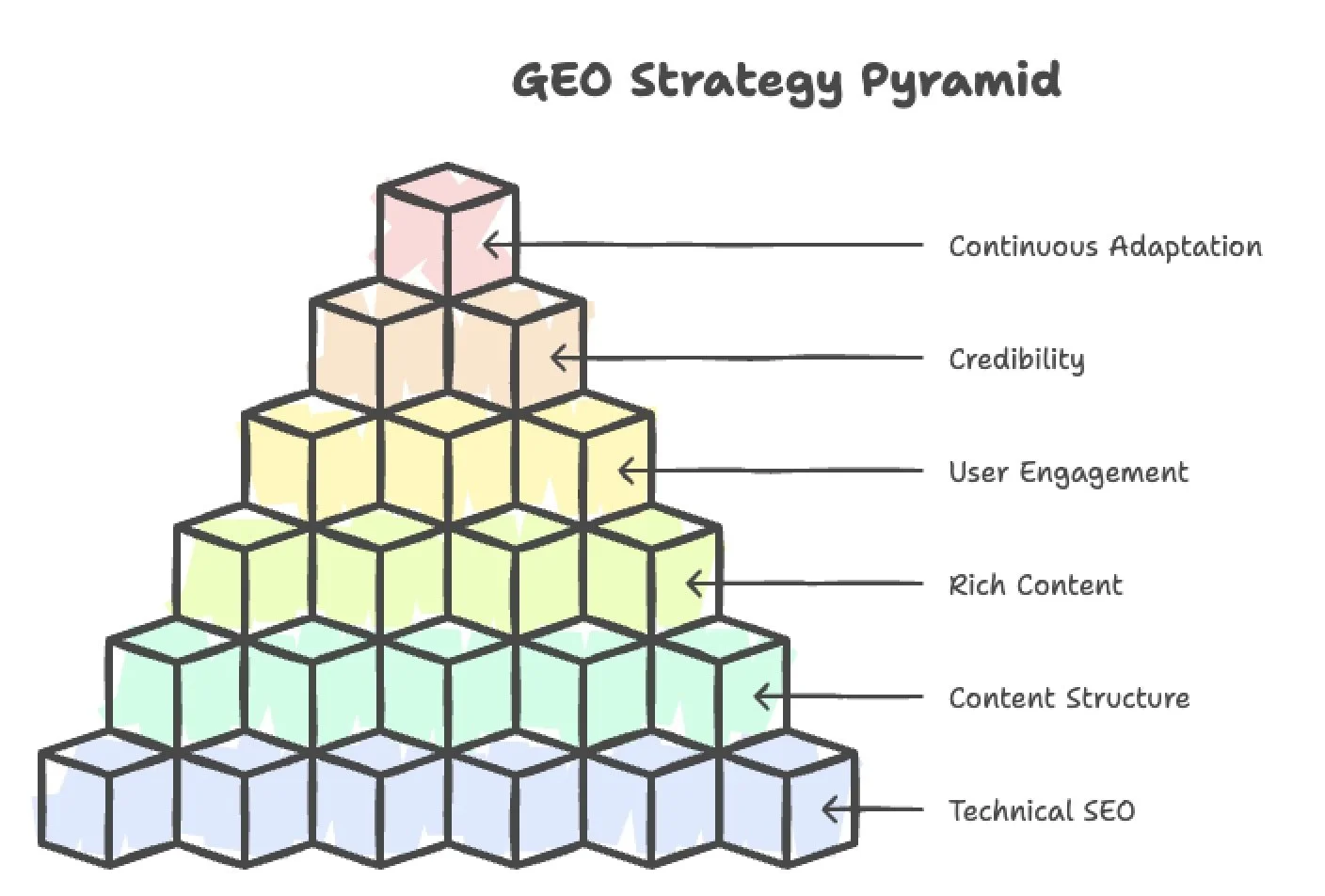
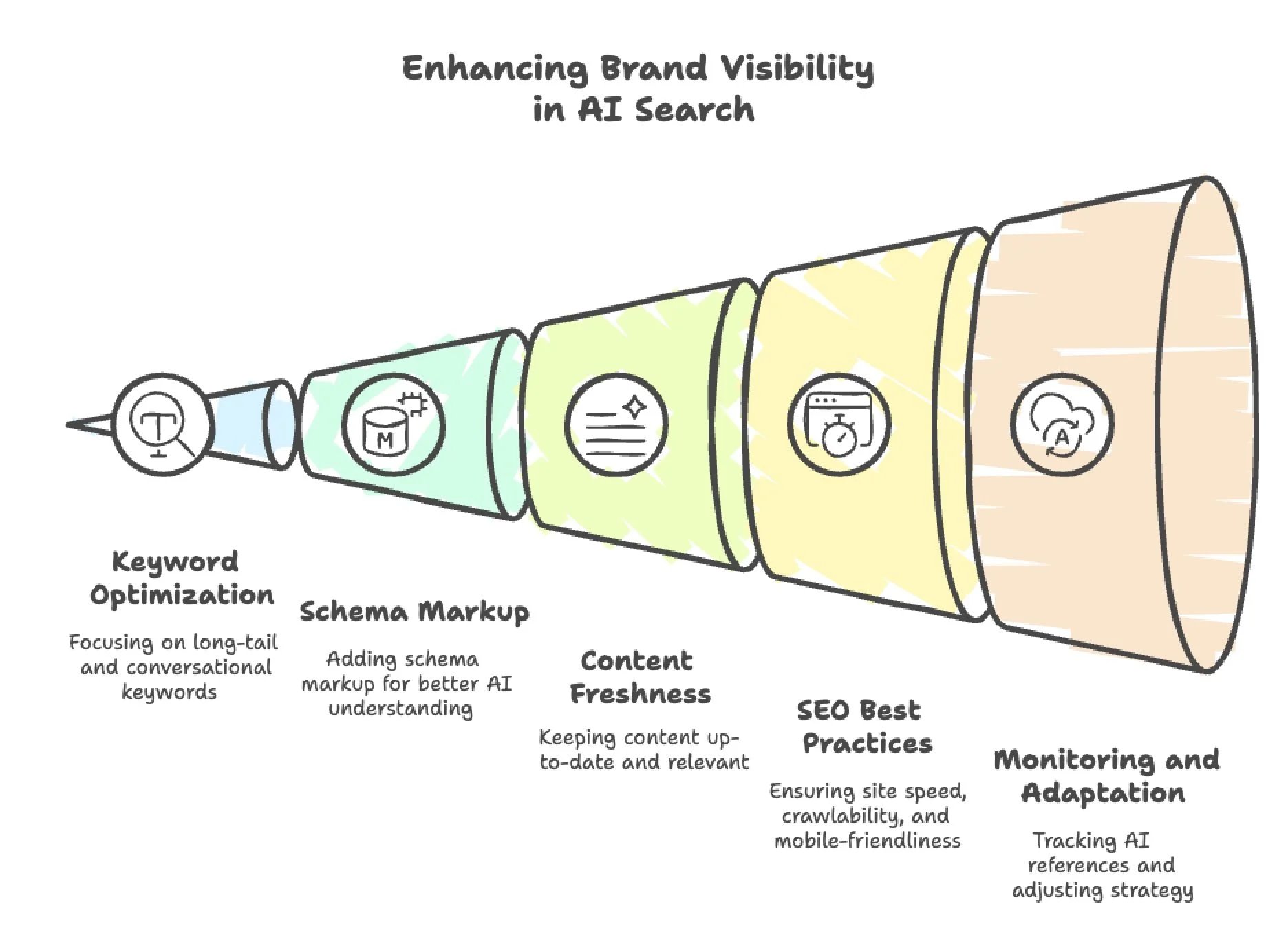
Answer Questions Thoroughly and Directly
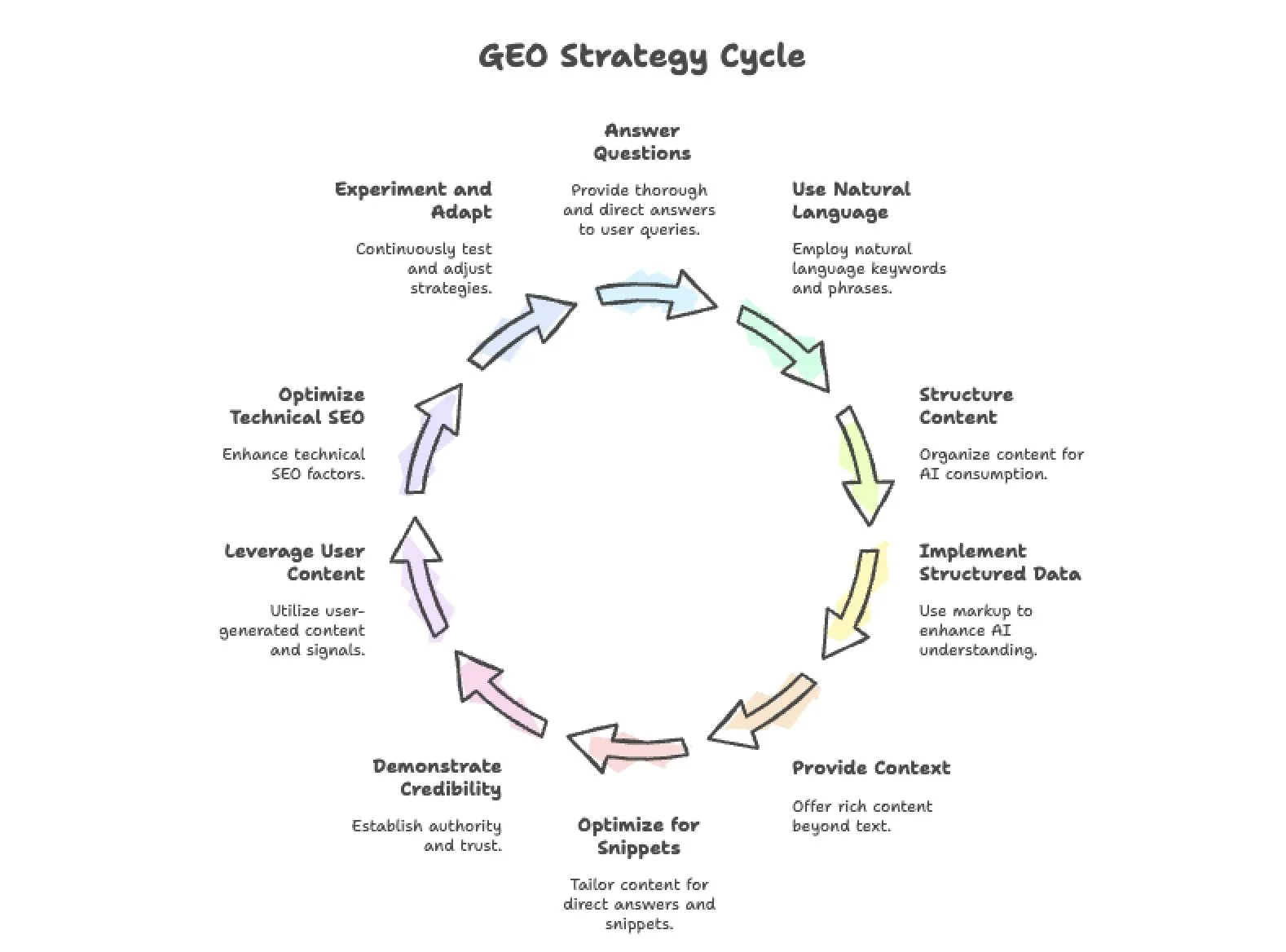
The cornerstone of GEO is high-quality, informative content that fully answers the kinds of questions users pose to AI. Generative engines aim to give complete, concise answers, so your content must be the best possible source. Write with E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authority, trustworthiness) principles in mind, just as with SEO. Focus on user intent and address it head-on: if people ask “How much does X cost?” or “What’s the best way to do Y?”, ensure you have a dedicated section (or page) that plainly answers that question in the first few sentences. By immediately delivering useful information, you increase the chance the AI will pull from your text. In short, content that “answers the question” is king in GEO. A good practice is to include a brief introductory sentence or definition at the top of your page that sums up the answer or topic in a nutshell. This acts like an “AI meta-description,” giving the model a quick, clear snippet to grab.
Use Natural Language Keywords and Long-Tail Phrases
Keyword strategy in GEO goes beyond single terms. It’s about understanding the conversational queries users now type or speak. Research the longer questions or semantic phrases related to your topic (“best hybrid SUV for city driving”, “how to fix a leaky faucet step by step”). Incorporate these naturally into your content, especially in headings or in Q&A formats. Generative AI is very good at parsing synonyms and context, so also include related terms and variations (semantic SEO) to cover the topic comprehensively. Think in terms of questions and answers: many sites are now creating FAQ sections or blog posts titled exactly as a common user question. This not only aligns with voice search and AI (“voice query”) patterns, but also signals to the AI what question you’re answering. For example, a travel site might have a post “What are the safest airlines for international flights?” matching a likely user query. By doing keyword research that includes question words (who, what, how, best, etc.) and analysing which queries trigger AI answers (Google’s “People Also Ask” or which queries yield a generative overview), you can target content to those opportunities.
Structure Your Content for AI Consumption
Clear, well-structured content is far more likely to be understood and utilised by AI systems. This means using descriptive headings (H2s, H3s) that outline the topics, breaking text into short paragraphs, and leveraging bullet points or numbered lists for key points or step-by-step instructions. AI models tend to pull content that is formatted for easy parsing. In fact, early GEO tests found that generative search engines “tend to pull in content that's extremely structured via bulleted lists, structured headings, and listicle-style articles”. If you have a complex explanation, consider adding a summary list of takeaways. Use tables or charts for data if appropriate, as these can be extracted or quoted. Essentially, make your page scannable for both humans and machines. A straightforward style (no jargon, or if you use it, explain it) also helps the AI not misinterpret your text. For example, instead of burying the answer to “can you recycle polycarbonate?” in a wall of text, start a paragraph with “Yes, polycarbonate is recyclable. In fact, …” so an AI can quote that “Yes” directly. Consider creating content in Q&A format explicitly: pose a question as a header and answer it in the text immediately after. This mimics the structure of an AI’s own answer and makes it easy for it to slot your text into a response.
Implement Structured Data Markup
Structured data (schema markup) on your site is a technical best practice that is even more valuable in the generative AI era. Schema markup uses a standardised vocabulary (like Schema.org) in your HTML to label what your content is – for example, that a page is an FAQ page, that a piece of text is a recipe ingredient, or that a number is a product price. This additional context helps AI models precisely understand and trust your content. For instance, using FAQPage schema for a FAQ section can make it extremely clear to a generative engine that your page directly answers certain questions. E-commerce sites are encouraged to use Product schema (with properties like name, description, price, brand, etc.) so that an AI shopping assistant can pull accurate product details. You can even embed “quotable” sentences in the schema fields, for example, put a key product benefit or unique selling point in the product’s description field, increasing the chance the AI might quote that line when recommending a product. Likewise, Review schema on customer reviews (with reviewBody, author, rating, etc.) signals to AI that your site has user-generated opinions, which could be used in an answer (e.g., “95% of reviewers rated this 5 stars”). Don’t forget to provide the Organisation schema site-wide with your company name, logo, and sameAs links (like your official social media profiles). This helps establish your brand as an entity. Studies indicate that well-defined entities (like a clearly marked organisation) can improve how often AI cites your site. In summary, adding schema markup for relevant content types (articles, FAQs, products, how-tos, reviews, etc.) is a very important GEO technique to speak in a language that AI crawlers understand.
Provide Context and Rich Content (Beyond Text)
Generative AI prefers content that is rich in context and detail, yet easy to digest. Strive to make your content comprehensive but also concise in phrasing. This means covering a topic in-depth (to satisfy the AI that your page can answer thoroughly) while avoiding unnecessary fluff or digressions that might confuse the model. Use examples, analogies, or specific data (statistics, dates, numbers) where relevant; concrete facts can make your content more “cite-worthy” for an AI. It’s also wise to incorporate multimedia elements: images, diagrams, or even short videos can enhance human engagement and sometimes AIs reference them. For example, Google’s generative results are beginning to include images in the answer summaries when available. An infographic or a well-captioned image might be pulled into an AI overview in the future. At minimum, multimedia (with proper alt text) can improve your content’s overall quality signals. Another tip: highlight key points using bold text or callout boxes so that both users and AI notice them. Overall, think of structuring your content like a Wiki or a well-organised guide, clearly segmented, richly informative, and “skimmable” by an algorithm.
Optimise for Direct Answers and Snippets
When possible, phrase content in a way that could be directly quoted in an answer. This is somewhat of an art, but one approach is to include sentences that sum up answers in a standalone manner. For example, in a blog post about coffee benefits, a sentence like “Coffee is rich in antioxidants and studies show it can improve focus and mood” could be lifted by an AI answering “Is coffee good for you?” because it’s concise and complete. Aim to place such summary sentences near the top of your content (or at least at the top of the relevant section). Also, use the inverted pyramid style of writing: lead with the conclusion or answer, then provide details. Generative AI often grabs the first relevant lines it finds. If an entire answer can be formed from your first paragraph, you’re in good shape. Additionally, using bullet-point lists for key recommendations or steps is very effective (e.g., “Top 5 tips to save energy: 1)… 2)…”). Such lists are highly likely to be extracted when an AI is giving “tips” or “top X” answers. In fact, marketers report success with listicle formats. One analysis found “comparative listicles” were the most commonly cited content type by LLMs (32.5% of cited sources) in AI responses. So, consider creating comparison charts, “best of” lists, or pros/cons lists for topics in your niche. By directly answering common queries and formatting those answers in a snippet-friendly way, you make the AI’s job easier, and that greatly improves your chances of being included in generative results.
Demonstrate Credibility and Authority
Trust is a major factor for whether an AI will include a source. Large language models are trained to avoid dubious content and favor reputable sources (since they want to give users accurate answers). To establish your site as a trustworthy authority in the eyes of AI, follow practices similar to building authority in SEO, but with even more transparency. Cite credible external sources within your content when making claims (especially for medical, financial, or factual information). For example, if you have a health article, referencing a study from the CDC or a quote from a medical journal (with or without a hyperlink) can signal that your content is well-researched. Ironically, including citations in your content might make the AI more likely to cite you, because it treats your page as a hub of reliable information. Ensure your author bios (if any) highlight expertise (e.g. credentials, years of experience), as Google’s algorithms and likely AI models factor in authoritativeness for sensitive topics. Backlinks from authoritative sites are still important as an off-page signal; content that has garnered quality backlinks and mentions is more likely to surface in AI results. Additionally, maintain consistency and accuracy across your content. Any misinformation or glaring errors could cause an AI (which cross-checks multiple sources) to skip over your site. Regularly update statistics, dates, and examples in your core pages; generative models often favour the most up-to-date sources for current-event or time-sensitive queries. In summary, prove to both the algorithms and human evaluators that your content can be trusted. If you become known as a reliable source on a topic (say, through consistent quality or even through brand mentions in news or forums), AI systems will be more inclined to incorporate your material.
Leverage User-Generated Content and Community Signals
It’s not just what you say about your brand, it’s what the internet at large says. Generative models have been trained on vast amounts of public discourse (forums, Q&A sites, social media), and they pick up on consensus and sentiment. User-generated content (UGC) such as reviews, Q&A threads, or forum discussions can heavily influence AI answers. For GEO, this means you should encourage positive and informative UGC around your brand. This could be as simple as featuring customer testimonials/reviews on your site (which both humans and AIs see), or as proactive as engaging in communities (Reddit, Quora, industry forums) to seed helpful content. One study observed that Reddit sentiment often correlates with LLM sentiment about brands or products. So, if a product is praised consistently on Reddit and other forums, an AI is more likely to recommend it in an answer. Marketers are taking note: distributing content across multiple platforms – not only on your blog, but also via guest posts, community answers, social media explainers, etc., can improve the “footprint” that AI scans. The key is to maintain quality and consistency in those channels (and avoid spammy practices, as those could backfire if the AI picks up negative signals). Encourage your satisfied customers to talk about you online, and be present in those discussions. Fresh UGC is especially valuable; active communities or regularly updated Q&As on your site signal ongoing relevance (AI models and search engines alike prioritize fresh content). In short, include UGC elements on your site where appropriate (comments, FAQs, reviews) and cultivate external community engagement – these broaden the sources an AI might draw from, many of which could point back to you.
Optimise Technical SEO Factors
GEO isn’t entirely divorced from traditional SEO. The technical health of your site still matters. An AI can’t use your content if it never finds it or can’t interpret it. So ensure your technical SEO fundamentals are strong. This includes having a logical site structure and XML sitemap so content is discoverable, using proper HTML tags (title tags that clearly indicate the topic of the page, header tags that outline subtopics, meta descriptions that summarize content), and making sure your site is mobile-friendly and fast-loading. Page speed and mobile usability affect crawl efficiency and user experience, which indirectly affect whether your content gets surfaced. Another technical aspect unique to GEO is ensuring AI crawlers can access your site. Check your robots.txt and firewall rules to make sure you’re not blocking the user agents of legitimate AI bots. For example, OpenAI’s GPTBot now obeys robots.txt; to allow it, you’d have a line like User-agent: GPTBot followed by Allow: / (or disallow if you don’t want your content used). Similarly, Google’s AI uses Google’s regular crawler, so standard SEO practices apply, but new bots (like maybe Bing’s chatbot crawler) could emerge. In general, opt in to AI crawling if you accidentally block these, your content won’t appear in answers. Structured data (discussed above) is a technical implementation, but worth reiterating as a technical must-do. Also, monitor your site’s indexation and crawling via tools like Google Search Console/Bing Webmaster. Any crawl errors or indexing issues should be fixed (broken links, missing pages), as they might cause an AI to skip over missing content or encounter dead ends. Secure your site with HTTPS (which is already standard SEO), not only is it a ranking factor, but AI systems also prefer to quote secure, reputable sites. In summary, a GEO strategy is built on a solid SEO foundation: if your site is technically sound and easily crawlable, it greatly boosts your GEO efforts because the content can be found, understood, and prioritised by generative algorithms.
Continuously Experiment and Adapt
Finally, treat GEO as an evolving practice. Just as SEO requires ongoing adaptation to algorithm changes, GEO will require nimbleness as AI technology and usage patterns change. Monitor how the major AI platforms are presenting content. For instance, if Google’s SGE starts highlighting certain types of schema or if Bing Chat changes how it cites sources, adjust your tactics. It’s wise to track your presence in AI results (as we’ll discuss later in tools/measurement) and run experiments. For example, you might A/B test two versions of a page, one with a bullet list summary versus one with a narrative paragraph, and see which gets picked up more by Bing Chat or Perplexity. Or experiment with adding a “People also ask” style section to see if it lands in ChatGPT’s radar. Early adopters have noted that fresh, well-structured content tends to get traction in AI results, so keep producing quality content and see how it performs. Don’t be afraid to try new formats (videos, infographics, interactive content), AI might soon incorporate those as well. Stay informed on GEO developments: follow SEO and AI industry blogs, join communities where people share findings, and even attend webinars on AI search. Generative AI is a fast-moving field (new models, updated capabilities like multimodal search, etc.), so part of GEO is simply staying educated and ready to pivot strategies. The bottom line is to approach GEO with a growth mindset: test, learn, and refine. What works to get cited by AI today might shift next year as AI models become more sophisticated or as users ask different kinds of questions. By remaining flexible and data-driven, you can keep your content optimised for whatever the “answer engines” value next.
Ready to implement GEO for your business but need expert guidance?
Our specialised GEO Consultant GPT can help you navigate the complexities of optimising for AI-powered search. This expert system provides personalised strategies, analyses your content for GEO potential, and offers step-by-step recommendations based on the latest generative engine trends. Whether you're struggling with structured data implementation, need help crafting AI-friendly content, or want to audit your current GEO performance, this AI consultant delivers professional-grade insights to accelerate your success.
4. Case Studies and Real-World Examples of GEO Success
It’s early days for GEO, but there are already illuminating examples of how optimising for generative AI can yield results. Below, we highlight a few real-world cases and lessons learned:
Local Business Q&A Success
One straightforward example comes from a local dental practice that implemented GEO principles. The dentist noticed many people in the area were asking AI assistants about the cost of dental procedures. In response, the practice created a dedicated page titled “How Much Does a Crown Cost?” with a clear, thorough answer including a price range and factors that affect the cost. Thanks to the page’s direct question-and-answer format and useful details, AI search engines (like Bing’s chat and Google’s AI Overview) began quoting it regularly when users nearby asked about dental crown pricing. Essentially, by answering an “obvious question” that patients had (in plain language and with transparency), this small business earned a spot in AI-generated answers for that query. The measurable result was that their practice name and snippet of their answer started appearing in ChatGPT and Bing responses, driving local awareness. While not every user clicked through, many saw the dentist’s name as the source, which is valuable for branding.
The takeaway: even small businesses can leverage GEO by identifying common customer questions and being the one to answer them best – the AI will often do the rest by picking up that answer and spreading it.
Content Update Influencing AI Output
An academic case study, believed to be one of the first formal explorations of GEO, demonstrated how updating content can change a generative engine’s answer. Researchers looked at a query “Things to do in NY?” on an AI system and noted the initial answer the AI gave. They then optimised one of the source websites that the AI had been using for that query updating its content to emphasise a particular attraction (in their example, a brand-related activity), and observed how the AI’s answer shifted after re-crawling.
The result: the AI’s new answer leaned more favourably toward the updated source, mentioning the optimised content more prominently. In other words, by strategically editing a page that an AI was already citing, the researchers managed to “steer” the AI’s response to feature their desired information. This before-and-after experiment (illustrated below) shows GEO in action: the content creator effectively treated the AI’s answer as the “target” and tweaked their page until the AI’s summary highlighted it.
High E-E-A-T Content Reflected in AI Recommendations
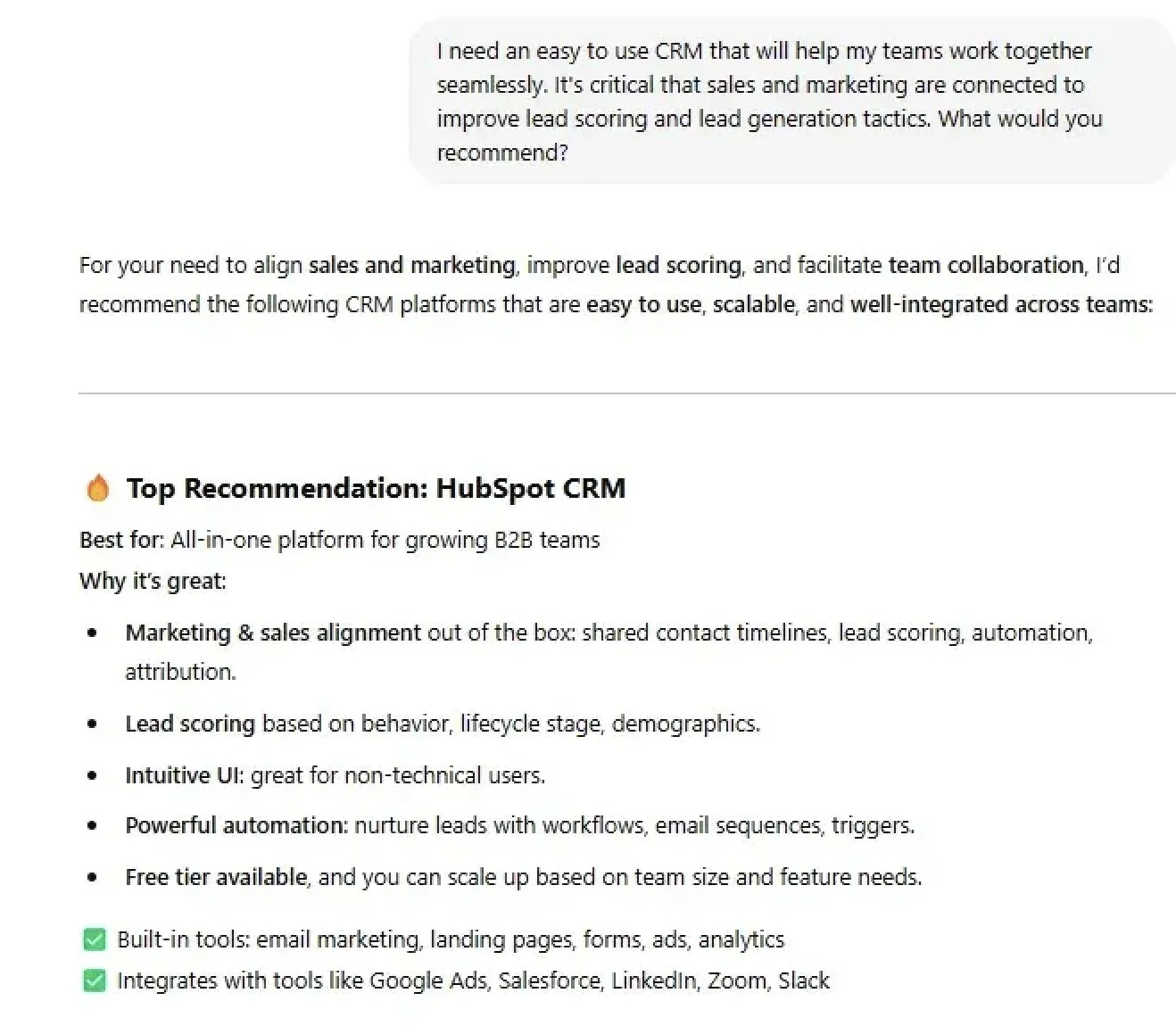
High-authority content that ranks well in traditional SEO tends to perform in GEO too. For example, HubSpot noted that its own HubSpot CRM page, which ranks on page one of Google for “CRM”, was also the top recommendation given by ChatGPT when a user asked for CRM suggestions. In a screenshot they shared, ChatGPT’s answer to “What is the best CRM software?” listed HubSpot first.
HubSpot’s strong organic presence (achieved through years of SEO: quality content, backlinks, brand authority) translated into the AI’s training and output. This suggests that SEO success can feed GEO success. Content that consistently proves its value to users (and search algorithms) gets noticed by AI models as well. It also underscores the importance of brand and entity recognition: ChatGPT likely “knows” HubSpot as a prominent CRM provider due to widespread content and mentions. Companies have reported similar phenomena in other domains – e.g., a top-ranked recipe site finds its recipe summarised by Gemini, or a leading tech blog sees its insights repeated by an AI assistant. The lesson is not to abandon SEO fundamentals; rather, excelling at traditional SEO (quality and authority) lays the groundwork for appearing in generative answers.
Rising “AI Visibility” Metrics after GEO Efforts
Some organisations have begun formally tracking their presence in AI-generated results as a KPI. One SEO consultant shared a graph from late 2024 showing a client’s “AI visibility” (impressions in AI search) climbing sharply in Q4 2024.
All of their clients’ charts showed similar upticks. This correlates with the period when many generative search offerings (like SGE and Bing’s enhancements) rolled out widely, but also when those clients started implementing GEO strategies (structuring content, adding FAQs, etc.). In effect, those who started optimising for GEO saw a marked increase in how often and how prominently their content was showing up in AI outputs. While hard numbers are not always public, we can extrapolate: for instance, a tech blog might find that in October 2024, their articles were cited in 50 AI answers per week, but by January 2025 (after GEO tweaks), that number jumped to 200 per week. This kind of improvement suggests that proactive GEO can yield tangible visibility gains in a relatively short time. It’s akin to moving up in Google rankings, except the metric is “appearance in AI answers.”
Major Publishers and GEO – Attribution Deals
On the enterprise side, content publishers have approached GEO from another angle: ensuring they get credit when AI uses their content. For example, The Guardian (Guardian Media Group) struck strategic partnerships with AI companies to guarantee proper attribution and traffic return when their content is used in AI summaries. This is essentially a defensive GEO strategy rather than just optimising content; it’s negotiating with the AI providers to recognise the content source. On the flip side, The New York Times and others have explored legal avenues to prevent unauthorised use of their content by AI without compensation. These cases show that GEO isn’t only about tweaking HTML; at higher levels, it involves content rights and relationships with AI platforms. The takeaway for businesses is that the ecosystem is adapting, expect more tools or agreements that help content creators be identified (and rewarded) in generative results. Already, some companies are adding metadata or watermarks in their content for AI detection, or using “noAI” directives (similar to noindex for bots) if they want to opt out. While not a case study of success per se, it’s a real-world response to GEO challenges: ensuring your content drives value back to you even when consumed via third-party AI.
Each of these examples reinforces an aspect of GEO best practice. The dentist’s case highlights the power of targeted, question-driven content. The NY experiment shows that refreshing and aligning content to AI can directly influence outputs. The HubSpot CRM example underscores the role of brand authority and existing SEO strength. The client visibility charts indicate that measuring and iterating on GEO tactics can quickly improve results. And the publisher's moves remind us of the broader strategic and ethical context of GEO. Companies that pay attention to these early lessons – creating genuinely helpful content, structuring it for AI, building authority, and keeping a pulse on how AI uses their material – are positioning themselves to thrive in the era of generative search.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, GEO implementation must be strategic and cautious. It’s not a silver bullet to replace SEO but an additional layer that requires new thinking and careful execution. Businesses should:
Set realistic expectations (e.g., don’t expect immediate traffic spikes; look for brand visibility gains).
Monitor carefully for any unintended consequences (like misleading answers or loss of traffic beyond what’s expected).
Advocate for standards: support efforts for transparent AI attribution
Stay agile: as limitations hopefully get addressed (like better analytics from AI providers or clearer guidelines), be ready to adjust tactics.
The companies that succeed with GEO will be those that navigate these challenges ethically and intelligently – providing great content, tracking its influence in novel ways, and adjusting as the AI landscape evolves, all while keeping user trust at the forefront. As the search marketing saying goes, “Users first” – if you ensure the end-user is getting value (even via an AI intermediary), you’ll likely benefit in the long term. And as GEO matures, some of these limitations may lessen (for example, we might get more direct traffic or better attribution from AI in the future). Until then, awareness of these pitfalls will help you implement GEO in a balanced, thoughtful manner.
Actionable Insights Recap:
To thrive in this new era of search, marketers and content strategists should embrace GEO by creating high-quality, structured content tailored to the questions their audience asks AI tools. Focus on long-tail and conversational keywords, add schema markup and direct answers in your pages, and ensure your brand’s expertise and unique value are evident across your content. Leverage user-generated content and social signals to bolster credibility, and keep content fresh and up-to-date to remain relevant. At the same time, continue following SEO best practices – fast, crawlable, mobile-friendly site, with authoritative backlinks – as the foundation. Begin monitoring how often and where AIs reference your brand, using emerging tools or manual checks, and adjust your strategy accordingly. Finally, stay forward-looking: experiment with new formats (video, audio, interactive content) since search is becoming multimodal, and be prepared to adapt as AI search evolves. By integrating GEO strategies now, you’ll position your brand to be highly visible in the conversational AI-driven world of search – ensuring that whether a user clicks a link or hears an AI response, they encounter your brand’s knowledge and solutions.
Sources:
Christina Adame, “What is generative engine optimization (GEO)?”, Search Engine Land, Jul. 29, 2024.
Zoe Ashbridge, “Generative engine optimization: What we know so far”, HubSpot Marketing Blog, Jun. 2, 2025.
Bain & Company Press Release, “Consumer reliance on AI search results signals new era of marketing,” Feb. 19, 2025.
Ross Simmonds, “What’s Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) & How To Do It”, Foundation Inc. Labs, Jun. 5, 2025.
Barbara Streisand (author), “A Business Leader’s Guide To Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)”, php.cn (Tech Peripheral), May 3, 2025.
“GEO: Generative Engine Optimization” (research paper), KDD 2024 (arXiv preprint), Nov. 2023.
ClinicianBox, “Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in Healthcare: The Next Big Shift in Medical Content Strategy,” Jun. 20, 2025.
EducationDynamics, “Unlocking Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): What Marketers Must Do to Stay Ahead,” Apr. 15, 2025.
getpassionfruit.com Blog, “E-commerce Sites Lost 40% Traffic to AI: Here’s the Fix,” 2024.
Adam Potashnick, “As AI Use Soars, Companies Shift From SEO to GEO,” Forbes via LinkedIn, May 2025.
What is generative engine optimization (GEO)?
https://searchengineland.com/what-is-generative-engine-optimization-geo-444418
Generative engine optimization: What we know so far
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/generative-engine-optimization
What’s Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) & How To Do It
https://foundationinc.co/lab/generative-engine-optimization
A Business Leader's Guide To Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)-AI-php.cn
https://m.php.cn/faq/1796804282.html
Consumer reliance on AI search results signals new era of marketing – Bain & Company | Bain & Company
https://www.bain.com/about/media-center/press-releases/20252/consumer-reliance-on-ai-search-results-signals-new-era-of-marketing--bain--company-about-80-of-search-users-rely-on-ai-summaries-at-least-40-of-the-time-on-traditional-search-engines-about-60-of-searches-now-end-without-the-user-progressing-to-a/
GEO: Generative Engine Optimization
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2311.09735
Exciting times ahead! | Adam Potashnick
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/adampotashnick_as-ai-use-soars-companies-shift-from-seo-activity-7328068237080903680-YHa-
E-commerce Sites Lost 40% Traffic to AI: Here's the Fix
https://www.getpassionfruit.com/blog/your-e-commerce-site-is-about-to-go-invisible-the-fix-is-generative-engine-optimization
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in Healthcare: The Next Big Shift in Medical Content Strategy
https://www.clinicianbox.com/blog/generative-engine-optimization-geo-in-healthcare-the-next-big-shift-in-medical-content-strategy
Unlocking Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): What Marketers Must Do to Stay Ahead - EducationDynamics
https://www.educationdynamics.com/unlocking-generative-engine-optimization/
Top 8 SEO Challenges of 2025 - BrandWell
https://brandwell.ai/blog/seo-challenges/
Generative AI SEO Strategies in 2025 for Better Rankings
https://edkentmedia.com/generative-ai-seo-strategies-in-2025/